LINEAR VS CIRCULAR
TRANSITIONING FROM LINEAR TO CIRCULAR
Transitioning from a linear to a circular economy involves rethinking the entire lifecycle of products, supply-chains and how we collaborate. Here we try and briefly navigate the differences between what is a linear vs a circular economy, and the key characteristics each includes.
No company becomes 100% circular in one go - but implementing small initiatives in your operations can have a big impact.
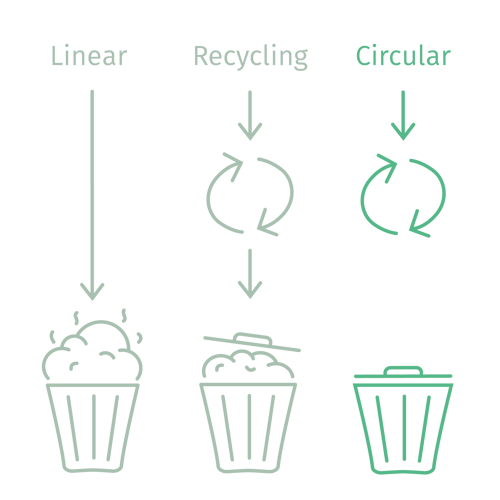
SO WHAT IS A LINEAR ECONOMY?
In a linear economy, the traditional model of production and consumption follows a "take-make-dispose" pattern:
Resources are extracted from the earth to manufacture products.
And plastic is extracted from non-renewable resources.
KEY CHARACTERISTICS OF A LINEAR ECONOMY

In a linear economy, we extract raw materials to fuel our production of new product. This constant demand for new resources puts pressure on natural ecosystems and over time leads to the depletion of our finite natural resources.

In a linear economy, products are often designed for short-term use - made with lower quality materials which results in items that quickly wear out, requiring frequent replacements. Which overall incentives us to continuously buy new products.

Once products have served their short-term purpose, they are now simply thrown away without reuse or recycling. This approach means that valuable materials are lost and end up accumulating as waste. The result is an unsustainable buildup of discarded products and a continuous need for new resources.
DO YOU NEED HELP MAKING THE TRANSITION FROM LINEAR TO CIRCULAR?
Contact us to discover how insights from AION can inform this transition!AND WHAT IS A CIRCULAR ECONOMY?
A circular economy aims to decouple economic growth from resource consumption by promoting a regenerative and restorative approach to production and consumption. A truly circular economy includes several factors - and is not just recycling! The circular economy offers economic opportunities through innovation, job creation, and the development of new business models centered around sustainable practices.
Products are designed to be durable, repairable, and recyclable from the outset.
With a focus on design, we can eliminate the concept of waste.
Circulating products and materials at their highest value means maintaining their use through reuse, repair, and maintenance.
By keeping products and materials in use, less resources is required for sourcing virgin raw materials. Decoupling economic activity from material extraction by keeping materials in circulation after use means more resources can be returned to nature.
KEY CHARACTERISTICS OF A CIRCULAR ECONOMY

Using recycled materials reduces reliance on virgin resources and minimizes waste. By repurposing materials that have already served a purpose, we keep resources in use and lower the environmental impact. This approach demands more from us when designing our products, to think of the end-of-life and materials from the start.

Products designed to last helps reduce the need for frequent replacements. Their durability ensures that products can be used repeatedly over time, which conserves resources and lowers overall waste. In a circular economy, this longevity not only provides economic value but also reinforces a sustainable approach to production and consumption.

Repair, repurposing, and recycling to extend the life of products beyond their initial use. By fixing and modifying items, we give them a new use rather than discarding them. Recycling breaks products back into raw materials, which in a final step can then be used to create new goods, ensuring that valuable resources continue to circulate within the economy.
Overall, while a linear economy follows a linear flow of resources from extraction to disposal, a circular economy aims to create a closed-loop system where resources are continually reused and recycled, leading to more sustainable and resilient economic growth.
CUSTOMER CASE STUDY
Discover how AION customers are transforming their business
Linear Vs. Circular FAQs
AION plays a role in closing the loop of material flows by setting up closed-loop supply chains and promoting the reuse and recycling of materials. Through our circularity, we facilitate the repurposing of waste materials into new products, ensuring that resources are kept in use for as long as possible.

